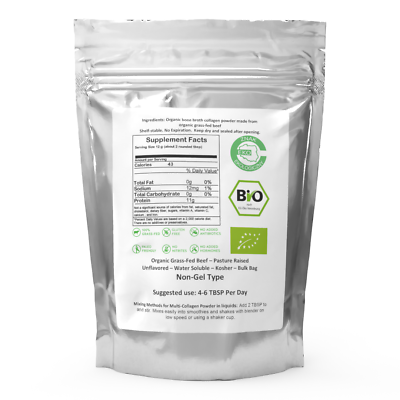
Bone Broth Powder – Pure Protein Organics – Grass-fed (300g)
$11.58 (-40%)
Bone Broth Powder – Pure Protein Organics 300g
Cold water soluble – Easy to mix – Mix in shakes, smoothies or juice
Organic Grass-fed pasture raised, No hormones, No antibiotics, No feed lots
Support joints, skin, muscles, digestion, and reduces
signs of wrinkles and aging
Rapid absorption. Helps regulate the body’s metabolism and enhances fat burning while you sleep
Kosher, Dairy Free, Soy Free, Grain Free, Gluten Free and
Unflavored
Best sports protein for preventing injury, faster recovery time, and building strong bones muscles, tendons and ligaments.
Bone Broth Collagen powder is a unique pure complete protein
and the building material to renew cells in all areas of the body including:
the hair, skin, nails, eyes, teeth, cartilage, bones, tendons, organs,
arteries, blood vessels, hemoglobin, immune cells and the immune system. There
are twenty eight different types of collagen that have been discovered .Not all
have been researched and some are in private testing in the medical fields for
stem cell research. Research does show us that if collagen types 1, II and III
are available in the body at the same time, the body can reproduce all twenty
eight types as the body needs it. However, if Collagen does not have enough
Vitamin C available to this process, it will remain a pro-collagen. (A
pro-collagen is a precursor to collagen, not collagen itself, and needs the
correct environment for the body to convert it into collagen). Vegetarians
often look to pro-collagen sources. Vitamin C is a vital nutrient required to
increase collagen production, while also providing stability and structure to
the collagen itself. Furthermore, amino acids must also be present to take this
delicate material from a pro-collagen structure to the actual collagen
material. Additional nutrients in large doses such as proline, glycine, lysine,
copper and manganese are all required to produce strong collagen fibers and
elastin. The common sources of gelatin at your local grocery store, touted as a
collagen source, are really pro-collagen because it is lacking the additional
components for the actual collagen material. See results in 2-6 months See
other listings in our Store Front for gelling products. Our simple bulk
packaging saves you not only money but it’s also efficient and avoids
unnecessary waste.
Bone Broth Collagen is the building block of healthy skin, joints, blood
vessels, hair and nails. Bone Broth Collagen forms the elastic fibers that
support youthful, vibrant-looking skin. As you age, your body’s collagen
deteriorates from use and exposure to free radicals. Proper collagen
supplementation rebuilds the body’s collagen. The skin regains its natural
elasticity. Joints heal.
Bone Broth Collagen is an anti-aging miracle. A scientifically proven collagen
dose: Studies on collagen powder show that most supplements don’t provide
anywhere near an adequate daily dosage. This Bone Broth Collagen powder is
formulated for the best results,
so each dose has 12,000mg of premium Bone
Broth Collagen hydrolysate
. We make Bone Broth Collagen a powder so it is
easy to use. It isn’t realistic to put 12,000mg of bone broth collagen into a capsule,
which is why no collagen pills on the market can provide an effective dose!
Bone Broth Collagen is a complete protein complex with all 20 Amino Acids
and all types of collagen that your body needs.
Many collagen supplements contain a limited profile of Collagen Types. Some
contain only Collagen Type II, found mainly in joints. Other products contain
only Collagen Types I & III, found mainly in the skin. Bone Broth Collagen
contains a complete collagen complex including Types I, II, III and up to 15
more collagen types, making it a perfect collagen supplement! Rated one of the
best collagen supplements available!
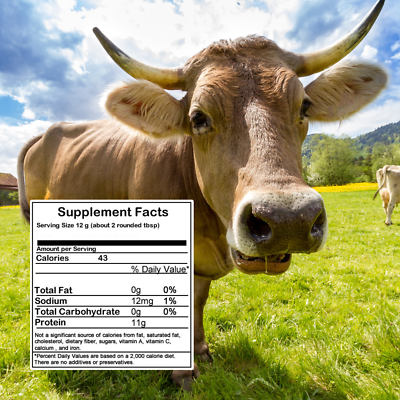
Amino Acid Content per serving
Serving size = 12g
(11 grams protein, 1g water)
Amino Acid
Percent
Milligrams per serving (+/- 10%)
Alanine
11
1,210
Arginine
9.3
1,023
Aspartic Acid
6.7
737
Cystine
0.1
11
Glutamic
Acid
11.4
1,254
Glycine
29
3,190
Histidine
1
110
Hydroxylysine
1.2
132
Hydroxyproline
14.5
1,595
Isoleucine
1.8
198
Leucine
3.4
374
Lysine
4.6
506
Methionine
1
110
Phenylanlanine
2.6
286
Proline
17.6
1,936
Serine
3.8
418
Threonine
2.2
242
Tryptophane
0
0
Tyrosine
1
110
Valine
3.3
363
The only ingredient is bone broth powder.
Naturally occurring in bone broth powder is an excellent protein source:
Amino Acid Content per serving: Serving size = 12g (11 grams protein, 1g
water)
Amino Acid
Percent / Milligrams
per serving:
Alanine 11%
1,211; Arginine 9.3% 1,025;
Aspartic Acid 6.7% 735; Cystine
0.1%
11; Glutamic
Acid 11.4% 1,255; Glycine 29% 3,192; Histidine 1% 108; Hydroxylysine 1.2%
130; Hydroxyproline
14.5%
1,597; Isoleucine 1.8% 200; Leucine 3.4%
372; Lysine 4.6% 507; Methionine 1%
110;
Phenylanlanine 2.6%
285; Proline 17.6%
1,937; Serine
3.8% 419; Threonine 2.2% 241;
Tryptophane
0% 0; Tyrosine 1% 111; Valine 3.3%
364 Trace amounts of bone minerals MCHC
Amino Acids Benefits
ALANINE
Non-Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic
Non-Polar, Hydrophobic – Aliphatic
Main Functions:
Important source of energy for
muscle.
The primary amino acid in sugar metabolism.
Boosts immune system by producing antibodies
Major part of connective tissue
ARGININE
Conditionally-Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic – Basic Side Chains
Main Functions:
Essential for normal immune system
activity.
Necessary for wound healing.
Assists with regeneration of damaged liver.
Necessary for production and release of growth hormone
Increases release of insulin and glucagon. Arginine is the most potent amino
acid in releasing insulin.
Assists in healing through collagen synthesis
Precursor to GABA, an important inhibitory neurotransmitter
Aids in wound healing
Decreases size of tumors.
Necessary for spermatogenesis.
ASPARTIC ACID
Non-Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic – Acid Side Chain
Main Functions:
Aspartic Acid is interconvertible
with Asparagine, and therefore the two amino acids have many functions in
common.
Increases stamina.
One of the two main excitatory amino acids, the other being Glutamate (Glutamic
Acid).
Helps protect the liver by aiding the removal of ammonia.
Involved in DNA and RNA metabolism.
Involved in immune system function by enhancing immunoglobulin production and
anti- body formation.
ASPARAGINE
Non-Essential – Proteogenic – Un-charged, Hydrophilic – Amidic
Main Functions:
Asparagine is made from Aspartic
Acid plus ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate).
One of the two main excitatory neurotransmitters. Glutamate, made from glutamic
acid, is the other. Among their functions as neurotransmitters, of particular
interest is the fact that Aspartic Acid and Asparagine have high concentrations
in the hippocampus and the hypothalamus. The hippocampus is a part of the brain
that plays the main role in short-term memory, while the hypothalamus is
involved in the biology of emotion, and serves as a neurological gate between
the brain and the rest of the nervous system.
Aids in removing ammonia from the body.
May increase indurance and decrease fatigue.
Detoxifies harmful chemicals.
Involved in DNA synthesis.
Probably stimulates thymus gland.
CYSTEINE-CYSTINE
Non-Essential – Glycogenic and Ketogenic
Un-charged, Hydrophilic – Sulfur-Containing
Main Functions:
Cysteine and Cystine are
interconvertible. Two molecules of Cysteine make Cystine.
Antioxidant.
Protective against radiation, pollution, ultra-violet light and other causes of
increased free radical production.
Natural detoxifier.
Essential in growth, maintenance, and repair of skin.
Key ingredient in hair.
One of the 3 main sulfur-containing amino acids, along with Taurine and
Methionine.
Major constituent of Glutathione, an important tripeptide made up of Cystine,
Glutamic Acid, and Glycine.
Precursor to the amino acid Taurine.
Precursor to Chondroitin Sulfate, the main component of cartilage.
GLUTAMIC ACID
Non-Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic – Acid Side Chain
Main Functions:
Glutamic Acid is a precursor to
Glutamine and GABA (2 neurotransmitters).
One of two excitatory neurotransmitters, the other being aspartic
acid/asparagine.
Excesses in brain tissue can call cell damage. This is thought to be one of the
mechanisms by why strokes kill brain cells; that is through the release of
large amounts of Glutamic Acid.
Helps stop alcohol and sugar cravings.
Increases energy.
Accelerates wound healing and ulcer healing.
Detoxifies ammonia in the brain by forming glutamine, which can cross the
blood-brain barrier, which Glutamic Acid cannot do.
Plays major role in DNA synthesis.
GLUTAMINE
Non-Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic
Un-charged, Hydrophilic – Amidic
Main Functions:
Precursor to the neurotransmitter
GABA. This is a vital function, as GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that
produces serenity and relaxation.
Important glycogenic amino acid, meaning that it is essential for helping to
maintain normal and steady blood sugar levels.
Involved with muscle strength and indurance.
Essential to gastrointestinal function; provides energy to the small
intestines. The intestines are the only organ in the body that uses Glutamine
as its primary source of energy.
Glutamine has the highest blood concentration of all the amino acids.
Precursor to the neurotransmitter amino acid Glutamate (Glutamic Acid).
Involved in DNA synthesis.
GLYCINE
Non-Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic
Non-Polar, Hydrophobic – Aliphatic
Main Functions:
Part of the stucture of hemoglobin.
One of the two main inhibitory neurotransmitters, the other being GABA.
Part of cytochromes, which are enzymes involved in energy production.
Inhibits sugar cravings.
One of the 3 critical glycogenic amino acids, along with serine and alanine.
Involved in glucagon production, which assists in glycogen metabolism.
HISTIDINE
Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic – Basic Side Chains
Main Functions:
Found in high concentrations in
hemoglobin.
Useful in treating anemia due to relationship to hemoglobin.
Has been used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
Precursot to histamine.
Associated with allergic response and has been used to treat allergy.
Assists in maintaining proper blood pH.
ISOLEUCINE
Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic and Ketogenic
Non-Polar, Hydrophobic – Aliphatic
Main Functions:
One of the 3 major Branched-Chain
Amino Acids (BCAA), all of which are involved with muscle strength, endurance,
and muscle stamina.
Muscle tissue uses Isoleucine as an energy source.
Required in the formation of hemoglobin.
BCAA levels are significantly decreased by insulin. Translation: High dietary
sugar or glucose intake causes release of insulin, which, in turn, causes a
drop in BCAA levels. Therefore, right before exercise, it is not wise to ingest
foods high in glucose or other sugars, as the BCAA’s, including Isoleucine will
not be readily available to muscles.
LEUCINE
Essential – Proteogenic – Ketogenic – Non-Polar, Hydrophobic – Aliphatic
Main Functions:
As one of the 3 branched-chain amino
acids (the other 2 being Isoleucine and Valine), Leucine has all of the
properties discussed with Isoleucine, as it pertains specifically to the
branched-chain amino acid functions.
Potent stimulator of insulin.
Helps with bone healing.
Helps promote skin healing.
Modulates release of Enkephalins, which are natural pain-reducers.
LYSINE
Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic and Ketogenic – Basic Side Chains
Main Functions:
Inhibits viral growth and, as a
result, is used in the treatment of Herpes Simplex, as well as the viruses
associated with Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, such as: Epstein-Barr Virus,
CytoMegalo Virus, and HHV6.
L-Carnitine is formed from Lysine and Vitamin C.
Helps form collagen, the connective tissue present in bones, ligaments,
tendons, and joints.
Assists in the absorption of calcium.
Essential for children, as it is critical for bone formation.
Involved in hormone production.
Lowers serum triglyceride levels.
METHIONINE
Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic
Non-Polar, Hydrophobic – Sulfur-Containing
Main Functions:
Assists in breakdown of fats.
Precursor of the amino acids Cysteine (and Cystine) and Taurine.
Helps reduce blood cholesterol levels.
Antioxidant.
Assists in the removal of toxic wastes from the liver.
One of the sulfur-containing aminos (the others being Cysteine and the minor
amino acid, Taurine). The sulfur-containing amino acids act as anti-oxidants
which neutralize free radicals.
Helps prevent disorder of hair, skin, and nails due to sulfur and anti-oxidant
activity.
Precursor to Carnitine,Melatonin (the natural sleep aid) and Choline (part of
the neurotransmitter, Acetylcholine).
Involved in the breakdown of Epinephrine, Histamine, and Nicotinic Acid.
Required for synthesis of RNA and DNA.
Natural chelating agent for heavy metals, such as lead and mercury.
PHENYLALANINE
Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic and Ketogenic
Non-Polar, Hydrophobic – Aromatic
Main Functions:
Precursor to Tyrosine, which, in
turn, is the precursor to the neurotransmitters: Dopamine and the excitatory
neurotransmitters Norepinephrine and Epinephrine.
Precursor to the hormone, Thyroxine.
Enhances mood, clarity of thought, concentration, and memory.
Suppresses appetite.
Major part of collagen formation.
While the L-form of all of the other amino acids is the one that is beneficial
to people, the
D and DL forms of Phenylalanine have been useful in treating pain.
DL-Phenylalanine is useful in reducing arthritic pain.
Powerful anti-depressant.
Used in the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease.
PROLINE
Non-Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic
Non-Polar, Hydrophobic – Aliphatic
Main Functions:
Critical component of cartilage ,
and hence health of joints, tendons and ligaments.
Involved in keeping heart muscle strong.
The main precursor to Proline is Glutamate.
Secondary precursor to Proline is Ornithine (minor amino acid).
Works in conjunction with Vitamin C in keeping skin and joints healthy.
SERINE
Non-Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic
Un-charged, Hydrophilic – Hydroxylic
Main Functions:
One of the 3 most important
glycogenic amino acids, the others being alanine and glycine.
Critical in maintaining blood sugar levels.
Boosts immune system by assisting in production of antibodies and
immunoglobulins.
Myelin sheath (the fatty acid complex that surrounds the axons of nerves is
derived from serine. One variation of Serine namely Phosphotidyl Serine, a
minor amino acid serves several important functions within the central nervous
system, including development of the myelin sheath. Multiple Sclerosis is one
of the so-called “De-myelinating Diseases.”
Required for growth and maintenance of muscle.
The amino acid Glycine is a precursor to Serine and the two are
interconvertible.
THREONINE
Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic
Un-charged, Hydrophilic – Hydroxylic
Main Functions:
Required for formation of collagen.
Helps prevent fatty deposits in the liver.
Aids in production of antibodies.
Can be converted to Glycine (a neurotransmitter) in the central nervous system.
Acts as detoxifier.
Needed by the GI (gastrointensinal) tract for normal functioning.
Provides symptomatic relife in ALS (Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Lou Gehrig’s
Disease).
In laboratory experiments with animals, Threonine increases thymus weight.
Threonine is often low in depressed patients. In that group of patients,
Threonine is helpful in treating the depression.
TRYPTOPHAN
Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic and Ketogenic
Non-Polar, Hydrophobic – Aromatic
Main Functions:
Precursor to the key
neurotransmitter, serotonin, which exerts a calming effect.
Effective sleep aid, due to conversion to serotonin.
Reduces anxiety.
Effective in some forms of depression.
Treatment for migraine headaches.
Stimulates growth hormone.
Along with Lysine, Carnitine, and Taurine is effective in lowering cholesterol
levels.
Can be converted into niacin (Vitamin B3).
Lowers risk of arterial spasms.
The only plasma amino acid that is bound to protein.
Tryptophan must compete with 5 other amino acids to pass through the
blood-brain barrier and enter the brain. Those 5 are: tyrosine, phenylalanine,
leucine, isoleucine, and valine and are called Large Neutral Amino Acids
(LNAA).
Requires pyridoxal-5-phosphate (P5P) a form of vitamin B6 to be converted into
serotonin. P5P deficiency will lower serotonin levels, even if Tryptophan
levels are normal.
TYROSINE
Conditionally Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic and Ketogenic
Un-charged, Hydrophilic – Aromatic
Main Functions:
Precursor to neurotransmitters
dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine (adrenaline) and melanin.
Effective anti-depressant for norepinephrine-deficient depressions. Tyrosine is
preferred over Phenylalanine, which is also a precursor to all of the above
neurotransmitters. Phenylalanine is one step removed from the metabolic
process, and can aggravate high blood pressure.
Precursor to thyroxine and growth hormone.
Increases energy, improves mental clarity and concentration.
Requires pyridoxal-5-phosphate (P5P) a form of vitamin B6 to be converted into
norepinephrine. P5P deficiency will lower norepinephrine levels, even if
Tyrosine levels are normal.
VALINE
Essential – Proteogenic – Glycogenic
Non-Polar, Hydrophobic – Aliphatic
Main Functions:
One of the 3 major Branched-Chain
Amino Acids (BCAA) . . .the other 2 being leucine and isoleucine . . . all of
which are involved with muscle strength, endurance, and muscle stamina.
BCAA levels are significantly decreased by insulin. High dietary sugar or
glucose intake causes release of insulin, which, in turn, causes a drop in BCAA
levels.
Competes with Tyrosine and Tryptophan in crossing the blood-brain barrier. The
higher the Valine level, the lower the brain levels of Tyrosine and Tryptophan.
One of the implications of this competition is that Tyrosine and Tryptophan
nutritional supplements need to be taken at least an hour before or after meals
or supplements that are high in branched chain amino acids.
Actively absorbed and used directly by muscle as an energy source.
Not processed by the liver before entering the blood stream.
Any acute physical stress (including surgery, sepsis, fever, trauma,
starvation) requires higher amounts of Valine, Leucine and Isoleucine that any
of the other amino acids.
During period of Valine deficiency, all of the other amino acids (and protein)
are less well absorbed by the GI tract.

 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Français
Français Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands